![Separator]()
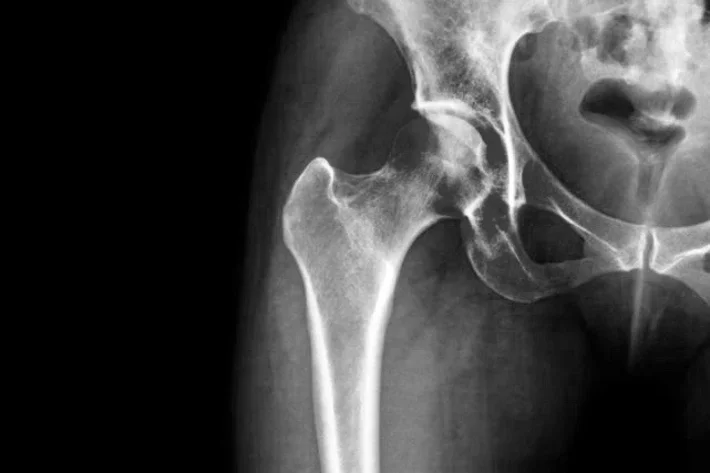
What are bone fractures?
Bone fractures, or broken bones, occur when a bone comes in contact with a force that causes it to break, split, or fracture. Fractures are most commonly caused by a forceful impact, and they’re more common in young children and the elderly than they are in young or middle-aged adults. This is because children are more likely than adults to participate in high-risk activities, while elderly patients tend to have more fragile bones.
Bone fractures can be grouped into four main categories: displaced, non-displaced, open, and closed. Displaced fractures occur when the bone breaks into two or more pieces that are in one way or another misaligned. Non-displaced fractures occur when the bone breaks, but the separated pieces remain in their proper alignment.
Open and closed fractures refer to whether or not the bone punctures the skin. When a fracture is closed, the bone breaks but does not pierce the skin, so there is no open wound. With an open fracture, on the other hand, the bone breaks through the skin, which can place the patient at risk of developing an infection.
Source:
WebMD